
Toxins found in the environment are known as environmental toxins. Environmental toxins are chemicals that can be both man-made and naturally occurring. They can impair our health by disturbing our biological functioning.
What are Examples of Environmental Toxins?
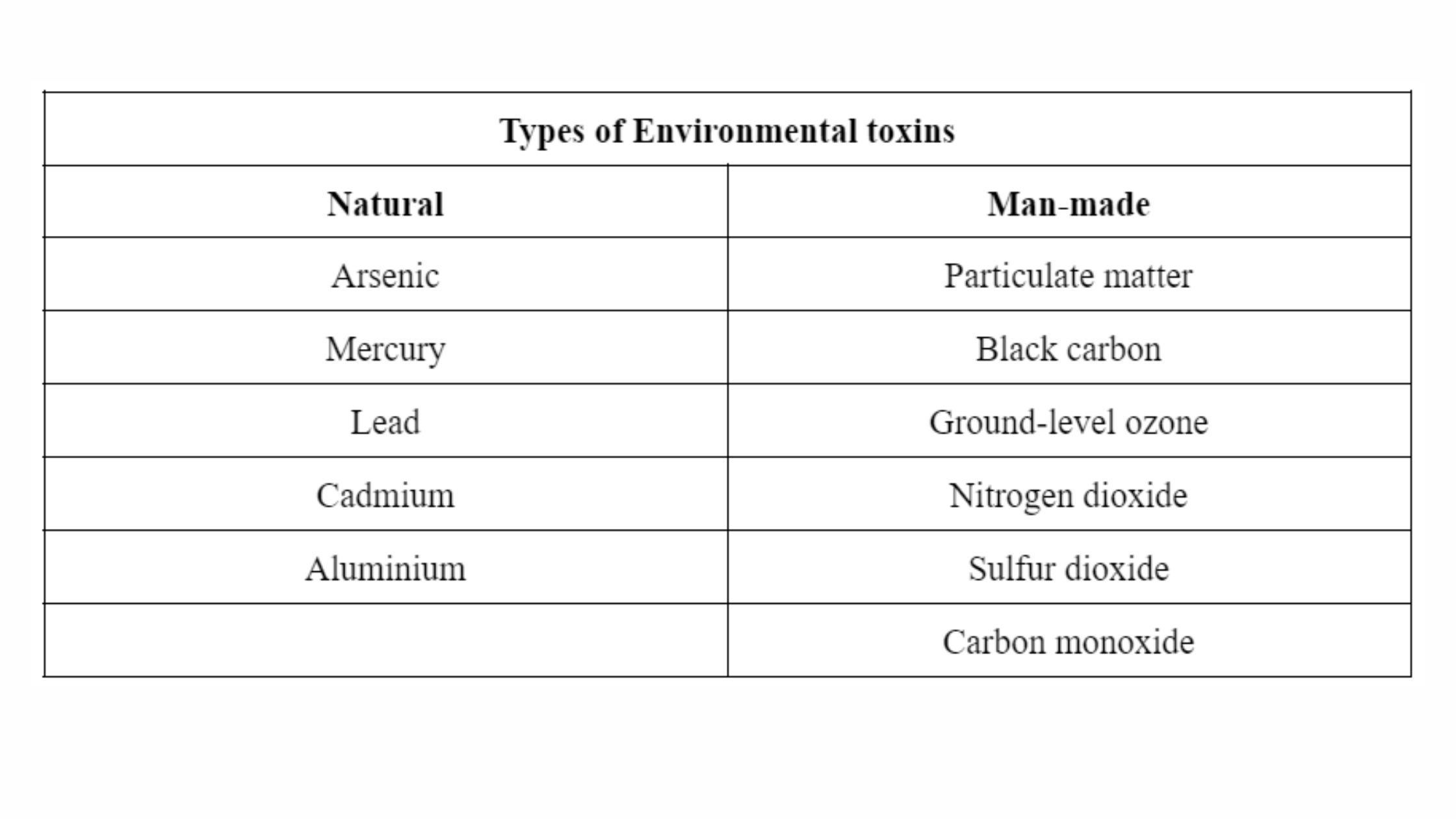
Toxic substances made up of organic (carbon-based) chemical compounds and blends are known as Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs). Industrial chemicals like PCBs and pesticides like DDT are among them.

What Are The Health Impacts of Environmental Toxins?
Toxins in the environment can have a negative impact on our health by interfering with normal organ functions.
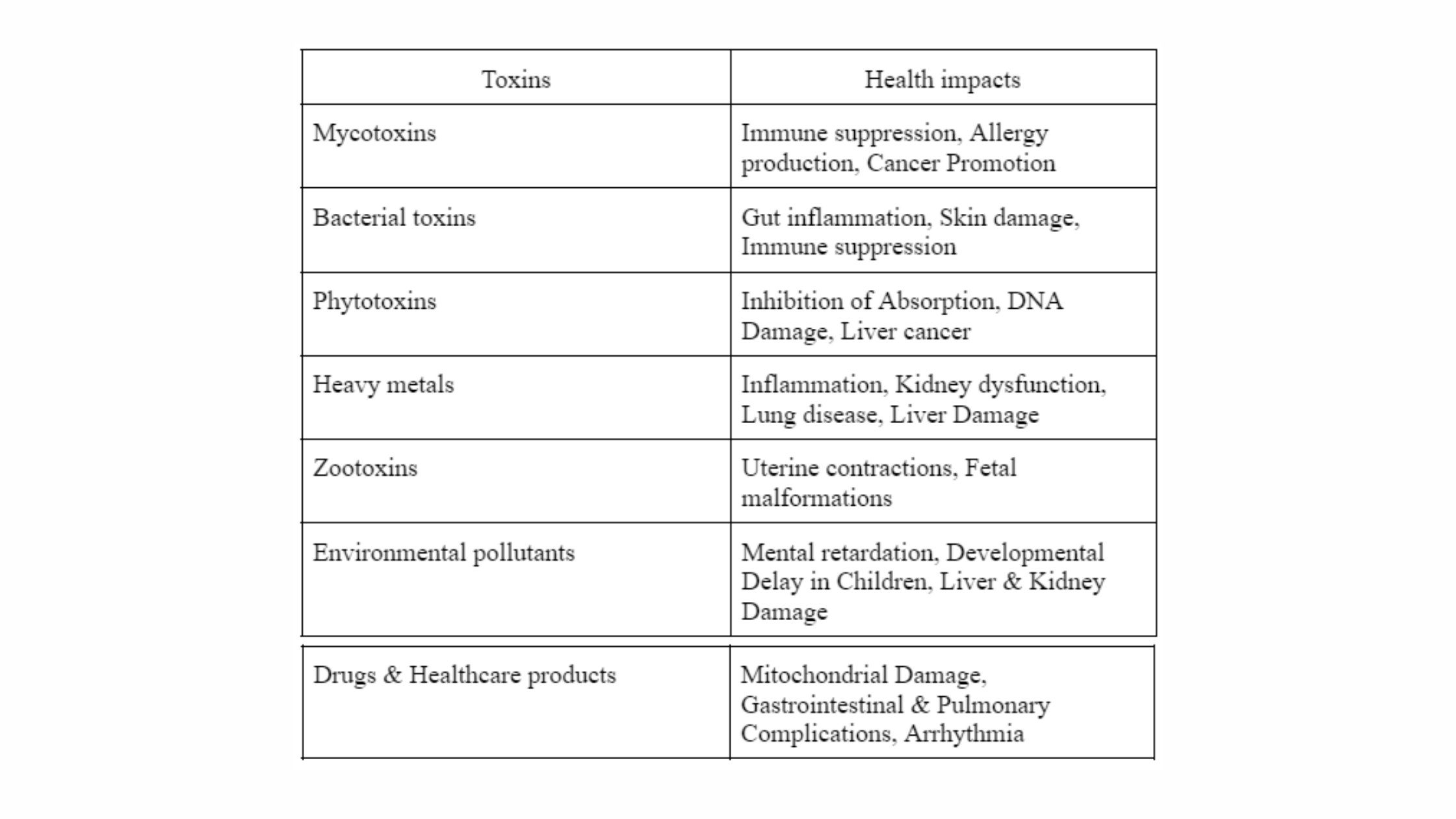
Health impacts of mycotoxins
Mycotoxins are poisonous substances produced naturally by some types of moulds (fungi). Mycotoxins-producing moulds can be found on a number of foods, including dried fruits, cereals, nuts, and spices.
Mycotoxins have a variety of detrimental impacts, including lowering immunity, triggering allergies, fostering cancer, and causing the leaky gut syndrome.
They also have antinutritional effects on nutrients like Vitamin A, Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, Iron, Selenium & Zinc.
Health impacts of Bacterial toxins
Bacterial toxins have been found to induce gut inflammation, skin damage, and respiratory and sensory disruptions. They can even suppress the body’s immunological response, making them dangerous for us. Bacterial toxins are also carcinogenic, meaning they can cause cancer in those who are exposed to them.
Health impacts of phytotoxins
Phytotoxins are harmful chemicals produced by plants or plant pathogens that inflict harm to living beings.
- Phytates, widely phytic acid, are antinutrients that prevent minerals including iron, calcium, phosphorus, and zinc from being absorbed.
- Furocoumarins (found in citrus fruits and carrots) are a type of natural food component that has the potential to harm DNA.
- Lectins are a type of glycoprotein that can cause toxicity in the gastrointestinal system by encouraging bacterial growth.
- Aflatoxins are responsible for up to 172,000 occurrences of liver cancer per year, the majority of which are fatal within months after diagnosis.
Health impacts of heavy metals
- Exposure to Arsenic found in pesticides & fungicides causes bronchitis, dermatitis & poisoning.
- Exposure to Cadmium found in pesticides, fertilizers, Cadmium & Nickel batteries can cause kidney dysfunction, lung disease, bone defects etc.
- Exposure to Lead found in paint, automobile emission, mining & burning of coal can damage the liver, kidneys and gastrointestinal tract.
Exposure to Mercury used in batteries, pesticides & the paper industry can result in tremors, gingivitis, minor psychological changes and even spontaneous abortion in pregnant women.
Health impacts of Zootoxins
Zootoxins are toxins that originate from animals. Animals can become dangerous if they collect hazardous substances in their tissues, exposing individuals, who try to eat them, to toxic exposure.
Some mechanisms by which zootoxins have been shown to adversely affect reproduction and development include stimulation of uterine contractions (scorpion venoms) and induction of fetal malformations (snake venoms).
Health impacts of environmental pollutants
Inhalation of environmental contaminants into the respiratory system may cause respiratory illnesses. They've also been linked to heart illness, reproductive and nervous system problems, and cancer.
Health impacts of Indoor Air Pollution
As people spend majority of their time indoors, domestic pollution is inevitable and detrimental to their health. During cooking, particulate matter concentrations in kitchens rise. One of the most common sources of indoor air pollution is vacuum cleaners. Allergic disorders affect 50 million Indians.
Solid fuel smoke, containing the majority of the toxins, present in tobacco smoke has been linked to a number of ailments. These include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), acute respiratory infection, and lung cancer (if exposed to coal smoke).
.png)
Health Impacts of POPs
- Increased risk of the respiratory tract, ear & gastrointestinal infections: As POPs weaken immunity, the risk of these illnesses increases.
- Carcinogenicity: Dioxin, a POP is a recognised carcinogen. It has the potential to cause cancer in humans.
- Endocrine disruption: Many chlorinated POPs have endocrine disrupting properties. They are responsible for the disruption of normal endocrine function.
- Estrogenic activity: Estrogenic action is found in the majority of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs), and various pesticides. These chemicals work in the same way that naturally occurring estrogens do, causing hormonal imbalance.
- Thyroid function suppression: Thyroid hormone production and function is hampered by dioxin, PCBs, and certain pesticides.
Health Impacts of drugs:
- Antibiotics like fluoroquinolones damage mitochondria, which are the powerhouses of human cells. Mitochondrial toxicity is a side effect of a wide range of medications. Antibiotics can pose a special threat to mitochondria because mitochondria share some features with their bacterial predecessors.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) usage can result in gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, hepatic, renal, brain and pulmonary issues.
- Bronchodilators can lead to osteoporosis, fractures, irregular heartbeat, and in certain circumstances, heart failure.
Environmental Toxins Which Can Affect Children:
Children are particularly vulnerable to the toxic effects of lead because, in comparison to adults, they absorb more lead toxins through the gastrointestinal tract. A higher proportion of systemically circulating lead reaches the brain (especially in children under the age of five), and the developing nervous system is particularly vulnerable to damage. Mercury is hazardous to the developing brain in the same way that lead is. Heavy metals, such as lead found in paint, pesticides, automobile emissions, mining, and coal burning, can cause mental retardation and developmental delays in children. The liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract can all be harmed by these heavy metals.
How To Avoid Environmental Toxins?
- Reduce the amount of antinutrients in your diet: Adopt methods like soaking overnight, germinating, milling, cooking and roasting.
- Reach for a mop: Dust contains lead, insecticides, and flame retardants. Sweeping or dusting your home may distribute pollutants into the air rather than removing them.
- Don't use bug spray: Pesticides, which are hazardous compounds used to destroy undesired insects or weeds, should be avoided. Keep your home free of food crumbs and spills. Instead of sprays, dust, or explosions, use baits and traps. Chemical tick-and-flea collars and dips shouldn't be used for your pets. To avoid the use and detrimental effects of chemical-based pesticides, employ natural organic insecticides on plants and farms.
- Avoid dry-cleaning clothes: Perchloroethylene (PERC) is a chemical used by most cleaners that can contaminate the air in your home. Instead, use water. The majority of "dry clean only" garments can be cleaned in water. Hand wash them or ask your dry cleaner to wet clean them for you.
- Check the weather forecast for air quality: Exercise as far away from sources of pollution as possible (such as traffic or factories) and avoid exercising outside on days when the air quality is poor.
- Attempt to stay distant from pharmaceuticals: To manage health issues, take a natural holistic approach with the assistance of functional nutrition.
Takeaway:
Toxins are all around us; we must learn to recognise them and limit our exposure to them as much as possible. Adopting healthy behaviors helps keep pollutants from influencing us and, as a result, averts health problems.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK215642/
- https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/iuatld/ijtld/2010/00000014/00000009/art00003
- https://www.phytojournal.com/archives?year=2018&vol=7&issue=6&ArticleId=6677
- https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-804239-7.00049-4
- https://refp.cohlife.org/when_antibiotics_turn_toxic.nature.2018.pdf
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114147
- https://doi.org/10.2165/00002512-200825050-00005
- http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/adc.2002.022202
- https://www.ucsf.edu/news/2011/01/103634/environmental-health-expert-offers-advice-how-reduce-exposure-toxins






.jpg)





